[D] I. GENERAL INFORMATION *
D2. Name and address *
D3. Other Business Locations *
D4. Type of Entity *
D5. URL *
D6. Identifier *
D7. Number of Employees *
D8. Revenue *
CORE Registrar Revenue *
Membership contributions *
D9. Directors, Officers *
(ii) Officers *
(iii) Managers *
(iv) (No ownership links) *
11. Subcontractors Listing *
Resources available within CORE's Membership *
Demonstrated Shared Registry Capabilities *
Separation of CORE Registry and CORE Registrar *
Enhancement of Existing CORE SRS and Protocol for new Registry Requirements *
Commitment to protocol convergence *
Redundancy through outsourcing and geographic distribution *
Competition between members in customer-related activities and value-added services *
Financial process *
Technical process *
D13.1. Detailed description of the registry operator's capabilities. *
D13.1.1. Company information. *
Legal Status *
Primary Location *
Membership *
(Formal Alliances) *
Competition between members *
Organizational Structure *
No ownership, equal voting power of members *
Shared Registry System Development *
Fully distributed business model *
Shared Registration System based on Registry Model *
Registrations in new generic TLD *
Development of a scalable shared registry system *
Second implementation of CORE SRS adapted to function as registrar system *
Duration of provision of services *
Experience with .com/.net/.org shared registry *
Internet-related experience and know-how available within membership *
D13.1.6. Management. *
D13.1.7. Staff/employees. *
Staff for registry activities *
CTO and CEO *
D13.2. Business plan for the proposed registry operations. *
Introduction *
Membership status needed to perform registrations, financial aspects *
Possible additional requirements *
Trust model and disciplinary framework *
User authentication by registrar *
Relationship with ICANN accreditation concept *
Cross-verification mechanisms *
Whois service *
Third parties with legitimate interests *
Complaint administration framework available (self-policing) *
Disincentive and special cost recovery charges *
D13.2.4. Marketing plan. *
Awareness programs and neutral information *
D13.2.6. Resources required to meet demand. *
Technical *
Staff *
D13.2.8. Staff size/expansion capability. *
D13.2.9. Availability of additional management personnel. *
D13.2.10. Term of registry agreement. *
D13.2.11. Expected costs associated with the operation of the proposed registry. *
D13.2.12. Expected revenue associated with the operation of the proposed registry. *
D13.2.13. Capital requirements. *
D13.2.14. Business risks and opportunities. *
D13.2.15. Registry failure provisions. *
D13.3. Pro-forma financial projections. *
D13.4. Supporting documentation. *
D13.4.1. Registry operator's organizational documents. *
D13.4.2. References. *
D13.4.3. Annual report. *
D13.4.4. Proof of capital. *
D13.4.5. Proof of insurance. *
D15. Introduction *
D15.1. Detailed description of the registry operator's technical capabilities. *
Systems development tools *
Outsourcing *
Significant past achievements *
D15.2.1. General description of proposed facilities and systems. *
Summary of system components *
Whois sites *
TLD Server sites *
Secretariat site *
Test SRS site *
Shared Registry Protocol *
Discussion of CORE SRS protocol choice, protocol convergence *
CORE SRS History *
Summary Database Schema *
Size, throughput, scalability *
Procedures for object creation, modification and deletion *
Registrar Transfer Procedures *
Grace Periods *
Change notification mechanism *
Reporting capabilities *
Verification *
Interface, User authentication *
Back-up *
Interface, User authentication *
Implicit Back-up *
Monthly statements and cross-verification *
Real-time remote logging messages *
Data Escrow *
Real-time remote logging on back-up srs site *
Daily backup within master site *
D15.2.9. System security. *
Physical security *
Technical security *
Data integrity *
Confidentiality *
Availability *
Network security *
SRS Site *
Whois servers *
TLD servers *
D15.2.13. System recovery procedures. *
Backup SRS site *
Support to members *
[D] Registry Operator's Proposal
Please place the legend "CONFIDENTIAL" on any part of your description that you have listed in item F3.1 of your Statement of Requested Confidential Treatment of Materials Submitted.
The Registry Operator's Proposal should be separately bound (if more than one volume, please sequentially number them) and labeled: "Registry Operator's Proposal." and must cover all topics described below. This page, signed on behalf of the registry operator, should be included at the front of the Registry Operator's Proposal.]
CORE is submitting an application to ICANN in this proceeding as a Sponsoring Organization for the .nom TLD and as a Registry Operator. CORE is submitting a detailed Section D as part of its .nom TLD Application. The MDMA believes that the information contained in CORE’s responses to the Section D questions in the .nom TLD Application will provide very detailed information to ICANN about its abilities to provide the registry operator services for the ..museum TLD.
MDMA’s responses contained herein may direct ICANN and interested participants in this process to additional information that may be found in CORE’s responses to questions in Section D of the .nom TLD Application, submitted to ICANN under separate cover.
E-mail address: tldapp@corenic.org
Note: CORE is an association whose members have their own marketing and customer service functions. CORE's members have offices in 20 countries on 4 continents and interact with customers in over 19 languages. (Please see attached.)
CORE's current membership qualification criteria are the same as those currently used by ICANN for registrar accreditation
CORE shared registry System (Düsseldorf, Germany): 5 staff provided by CSL GmbH
CORE Secretariat (Geneva, Switzerland): 5 staff provided by Axone SA
For the sake of comparison to existing gTLD registrars with centralised business models, CORE has made an approximate count of CORE member staff concerned with domain registrations via CORE. The approximate aggregate number of number employees concerned with CORE registrations is 200.
For the CORE-Registry operations, a directly employed staff of 10 is to be built up prior to launching its first TLD. This staff will partly be newly hired and partly be seconded from members of the Association.
Mr. Ken Stubbs, Chair
Dr. Jonathan Robinson, member of Executive Committee
Mr. François Luc Collignon, member of Executive Committee
Mr. Hal Lubsen, member of Executive Committee
Ms. Rosa Delgado, member of Executive Committee
Mr. Robert F. Connelly, member of Executive Committee
Mr. Werner Staub, member of Executive Committee and Head of CORE Secretariat
Siegfried Langenbach, Head of Shared Registry System (SRS) Operation and Development
Christoph Schiffer, SRS Operation and Development, Back-end systems
Marc Baradez, CORE Secretariat
Radek Maturana, CORE Secretariat
Cary Karp, Director
Department of Information Technology
Swedish Museum of Natural History
Svante Arrheniusv. 3
Box 50007
104 05 Stockholm
Sweden
Email: ck@nrm.se
Phone: +46 8 5195 4055
Fax: +46 8 5195 4235
2) J. Paul Getty Museum:
Kenneth Hamma, Assistant Director
The J. Paul Getty Museum
1200 Getty Center Drive
Suite 1000
Los Angeles, CA 90049-1687
Email: khamma@getty.edu
Phone: 310-440-7186
Fax: 310-440-7752
Please contact either or both of these individuals and they, in
turn, will contact the appropriate individuals at CORE.
- World class telecommunications companies (Cegetel, France Telecom, Deutsche Telekom, KPN, Saritel/TelecomItalia, Telia, Colt Telecom);
- Highly specialised domain name registrars, a large number of whom are already ICANN-accredited;
- ccTLD registry operators (in particular DENIC, the largest registry after .com with over 3 million domains under .de; NIC-SE concerned with ..se; DKNIC concerned with .dk);
- Internet Service providers;
and
- a standards organization (ETSI European Telecommunications Standards Institute). ETSI is the forum for key standards such as GSM and UMTS, and one of the four members of the ICANN´s PSO.
The co-operation of members through the CORE framework is limited to areas where shared resources are technically necessary. The shared resources are developed and managed by way of multi-lateral consensus building and fair sharing of costs.
CORE is committed to contribute to the convergence of shared registry protocols and concepts. However, CORE does not feel that the current RRP is an appropriate working basis. CORE is looking forward to work on a common shared registry protocol with ccTLD registries and new and existing gTLD registries, within the ITEF framework.
Value-added service by member registrars can be built upon instruments provided by the registry, such as the ability (available equally to all member registrars) to store optional information in the registry: PGP Public Keys, Personal Ids …etc.
As a Registrar organization, CORE is committed in contributing to converge on shared registry protocols. There is reason to expect productive dialogue between registries and registrars in this area as soon as the TLD application period ends. CORE will ensure that members can operate in compatibility mode and work with the registrar community at large to develop next generation protocols. There is a widely held view within CORE's membership that new protocols should give due consideration to recent standards such as XML and be developed on the traditional "rough consensus, running code" philosophy.
Before initiating registry operations, the association intends to split into a Registrar and a Registry. Under the current working hypothesis,this will involve the creation of a new association to which the assets and liabilities related to registry operations are transferred.
The CORE Registry will also be a not-for-profit Association under Swiss law.
The CORE Registry will also have its Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland. It is also expected that the main Registry Database will be hosted in Geneva. Additional database sites and points of presence may be located elsewhere.
| 001 | Nominalia | Spain |
| 003 | PSI K.K. | Japan |
| 004 | Internet Domain Registrars Corp. | Canada |
| 005 | First Identity Net | USA |
| 008 | Chungwa Telecom Co. Ltd | Taiwan |
| 009 | California Suncare, Inc. | USA |
| 010 | ETSI | France |
| 011 | CSL GmbH | Germany |
| 012 | TUCOWS International Corp. / Domain Direct | Canada |
| 013 | Melbourne IT | Australia |
| 014 | DENIC eG | Germany |
| 016 | NetBenefit (UK) LTD | United Kingdom |
| 017 | Interdomain, S.A. | Spain |
| 018 | Namebay S.A.M | Monaco |
| 019 | Pacific Communications Dev. Corp. | Taiwan |
| 020 | Aktiv GmbH | Germany |
| 022 | Global Internet Services, Inc | USA |
| 024 | Bahamas Telecommunications Corp | Bahamas |
| 025 | Corporate Domains, Inc. | USA |
| 028 | Net Wizards, Inc. | USA |
| 030 | Saritel S.p.A | Italy |
| 033 | IP Consult GmbH | Germany |
| 035 | Smartphone SA | Switzerland |
| 038 | Callisto germany.net | Germany |
| 039 | Knipp Medien und Kommunikation GmbH | Germany |
| 040 | Retevisión SA | Spain |
| 041 | Telia AB Network Services | Sweden |
| 043 | Alinet Italia Srl | Italy |
| 045 | Domain Names International, LLC | USA |
| 046 | Eurotel | Germany |
| 048 | LanMinds, Inc | USA |
| 049 | L.M. - Sitename Ltd | Israel |
| 050 | Médiafusion Inc. | Canada |
| 051 | Netlink Holdings Pty Ltd | Australia |
| 052 | Netlink Internet Services Ltd | United Kingdom |
| 053 | CASDNS, Inc. | USA |
| 054 | eNom, Inc. | USA |
| 056 | TotalNet Inc. Div. MPACT Immedia Inc | Canada |
| 058 | Internet Name Registrar | USA |
| 059 | The Edge Consultants Pte Ltd. | Singapore |
| 060 | France Telecom Transpac | France |
| 061 | Freedom Communications, Inc. | USA |
| 063 | Ji Tong Communications Co., Ltd. | China |
| 064 | SITA | Switzerland |
| 066 | Demon Internet Ltd. | United Kingdom |
| 068 | Epoch Networks | USA |
| 071 | Secunet Security Networks GmbH | Germany |
| 072 | Halo Technologies Ltd. | USA |
| 075 | Deutsche Telekom AG | Germany |
| 076 | Network Information Centre (NIC-SE) | Sweden |
| 077 | wespe.de GmbH | Germany |
| 078 | Domain Bank, Inc. | USA |
| 079 | Axone Services & Développement SA | Switzerland |
| 080 | Capital Networks Pty Ltd. | Australia |
| 081 | InterNetX GmbH | Germany |
| 082 | Grona Verket AB | Sweden |
| 084 | Tele Danmark A/S | Denmark |
| 085 | KPN Telecom BV | The Netherlands |
| 086 | Europe Online | Luxembourg |
| 087 | ARK Inc. | Japan |
| 088 | Tokyo Internet Corporation | Japan |
| 090 | InterQ | Japan |
| 091 | InterneXt | France |
| 093 | 7WAYS | France |
| 092 | Cegetel S. A. | France |
| 094 | Boston Light Software Corp. | USA |
| 095 | OLM, LLC | USA |
| 096 | Global Village GmbH | Germany |
| 097 | ABC TeleMedia AG | Germany |
| 098 | COLTTelecom AG, Switzerland | Switzerland |
| 099 | 3W-Media GmbH | Germany |
| 101 | Kamp Netzwerkdienste GmbH | Germany |
The IAHC process preceding the launch of CORE
The gTLD-MoU formalised an open public consultation process launched at the initiative of the Internet Society (ISOC), the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and the International Telecommunication Union in response to the explosive growth of the DNS. The need for additional top-level domains was also felt in the context of the full monopoly held then by Network Solutions, Inc. on the registration of generic top-level domains. The need to specify an alternative was also felt because the contract between Network Solutions Inc. and the US National Science Foundation wasdue to expire in March 1998.
Development of a scalable shared registry system
During the second half of 1997, 88 membership applications were approved. After the formal creation of CORE in October 1997, CORE started to build a shared registration system in 1997 in order to be ready for registrations by February 1998. This first version of an automated shared domain registry system based on the principle pre-payment was tested by a large number of CORE members. Extensive participation in ICANN process
In the context of CORE's ICANN registrar accreditation and selection in 1999 as a Testbed registrar for the newly shared .com/.net/.org registry, this system was adapted to operate as a shared registrar system.
At the time of writing, CORE's shared registration system handles over 800,000 domain names. Over 30 CORE members participate as so-called reselling members in CORE's current role of ICANN-accredited registrar.
CORE's current shared Registrar System is a variant of the second implementation of its SRS design. Both implementations of the CORE SRS have originally been developed as a full-fledged registry system.
The CORE SRS version used for .com/.net/.org is based on the second implementation of the CORE SRS developed in 1999. The interconnection with the NSI Registry took place in the framework of the NSI shared registry testbed for which CORE was selected as a "testbed registrar" by ICANN. It is important to point out that technically, a shared registrar system to be kept in synchrony with a "dorsal-spine-only" shared registry is more complex than a standalone registry. Moreover, CORE's work on the NSI interconnection could only start in June 1999 as NSI had not previously published its RRP protocol and at that time required a non-disclosure agreement and a performance bond before supplying any information.
Additional plausibility-checking, automated archiving and the SRS team and the CORE secretariat run verification tools. These systems are updated and improved continuously.
Despite its generally decentralized organizations, CORE relies on certain centralized verification mechanisms, such as those involved in domain holder changes. Experience with these mechanisms is key for CORE's proposals for distributed enforcement and verification mechanisms with a central audit electronic trail.
The biographies of the current executive committee members are attached. As a result of the projected separation of CORE's registrar and registry functions, the composition of the Executive Committee in charge of the registry at the start of operations may be different.
Also attached are biographies of several managers and technical experts who have already been identified as candidates who would be seconded by CORE members. CORE expects additional commitments from CORE members in the near future. For reasons of personal privacy and because the CORE membership at large has something to say in the choice of the candidates retained, the names are not for publication at this stage.
Given the immediate need for specialized managers and technical experts, CORE will primarily draw on membership resources to build the first nucleus of the Registry team. This will be based on seconding arrangements with members with a minimum duration of 1 year for senior positions and three months for junior positions.
As pointed out under 13.1.7, the attached CVs are not for publication at this stage for privacy and due process reasons.
A new policy is to be negotiated for the CORE Registry as soon as its separation from the CORE Registrar is complete.
This principle in many ways implies what products and services the registry operator offers to members and indirectly to end-users.
For historic reasons, the CORE association is currently active as a registrar for .com, .net, .org registrations. Given many members' and end-users' reliance on these functions, there is a need to continue these operations as a shared registrar. The shared registrar will therefore be separated from the newly created shared registry operator and may become a member of the latter.
The membership qualification criteria currently used by CORE is in principle identical to those practiced by ICANN for accreditation except that CORE accepts supporting documentation in several additional languages. It is expected that after the split the CORE Registry would continue to relay on member qualification criteria equivalent to those used by ICANN. Indeed, as explained in the S.O Proposal, CORE favors a gTLD wide ICANN Registrar accreditation program.
For registration in the .museum TLD, the registrar has to sign the policy document and be approved by the MDMA. The MDAM approval concept and the related registry access privileges may be differentiated by type of operation Additional information on MDMA’s policy on registration are found in section E of this proposal .
The registry in principle trusts its registrars and their due diligence in authenticating end-users. The registrars have the professional responsibility of submitting well-formed requests to the registry after reasonable verification as can be expected of a professional registrar in the specific circumstances. Failure to act professionally can lead to the member registrar being barred from certain transaction by decision of the registry operator or the MDMA.
Certain transactions, such as registrar transfers, are placed under cross-verification, random verification or systematic screening regimes.
User authentication by registrar
The responsibility to authenticate users is placed on the registrars. Thanks to this principle, registrars can compete in terms of quality of service and the overall concept becomes scalable. This principle does not exclude designs where registrars place customers' digital certificates or other verification resources into the central registry database for additional security.
If pre-screening is used and administered through the MDMA, the member registrar has the responsibility of submitting adequately pre-verified requests that can reasonably be expected to pass the screening hurdle. This is essential to keep the screening costs low and avoid irritation of end-users.
The registrars in turn interact with the public and/or with resellers. Depending on the model used for chartered TLDs, additional services may be provided in interaction with specific bodies designated by the MDMA (e.g. pre-screening mechanisms).
Types of information stored by the registry
Note: the technical plan contains a detailed description of information resources managed by the registry.
Domain, name server, holder, contact, and maintenance information
The array of registration services provided is significantly larger than that of the current .com/.net/.org shared registry. CORE Registry will not only host domain and name server information, but also domain holder contact and maintenance information, or agent for contacts information.
Additional records
Moreover, additional information required by the MDMA could also be stored in the registry. As the registry evolves, additional value-added records (such as public key certificate IDs or key fingerprints) may be stored in the registry by the registrar at the request of the end-user.
Direct pointers
From a technical standpoint, the registry has the ability of maintaining direct pointers to hosts, eliminating if need be the delegation via additional name servers managed by third parties.
Electronic document storage
In the context of some transactions, registrars can store electronic copies of supporting documents in the registry and reference them from within the domain or contact records.
Information to the end-user provided via the registrar
The registrar is the end-users partner for registration, but also for providing status information on the registration where the data cannot be published for privacy or other reasons. Data that is not published on the public Whois service can be checked through the maintaining registrar.
In the event that a domain holder wishes to perform a registrar change or wishes to check the data lodged in the registry without going through the maintaining registrar, a cross-verification mechanism is used. This mechanism is based on automated central procedures used to ensure that another registrar can only access a customer's information after having been specifically instructed.
An example of such a mechanism is the registry sending, at the request of Registrar B, a one-time password to the recorded customer address. The customer then can give this password to registrar B and obtain confirmation without having to go through the maintaining registrar A. This mechanism illustrates how important it is to store customer contact information centrally in order to foster competition between registrars.
CORE will operate a unified Whois service i.e., contrary to the current concept use for .com, .net and .org, users can find all the data on the central Whois service. The Whois is run on several machines independent from the registry database. They only provide information that can be shown in line with policies, ICANN guidelines and applicable privacy legislation as set forth in the registration policy.
For performance and availability reasons, CORE will eventually operate several Whois servers on different locations providing information on all the domains registered.
As the Whois servers are separate from the registry database, updates are sent from registry back-end system to the Whois server whenever a change is made. A given domain or contact record will thus show in the registry within 30 seconds. This technology has been successfully used on the CORE registrar Whois server and has performed well for over 1,500,000 domain, contact and host records managed by the current SRS used for CORE's registrar activity.
Some specialized servers will be provided to facilitate pre-registration check queries, i.e. queries whose purpose is to verify if a domain is still available in the registry.
Third parties with legitimate interests
The SRS has the ability to administer, on a granular basis, information requests from third parties with a legitimate interest. In this context, it keeps track of the requests and the information provided. The requests are administered by the maintaining registrar whenever possible. Based on automated cross-verification and supervision by the registry, it is possible to process request involving several registrars in a single request.
The policy of providing information to third parties is subject to the registration agreement, registration policy and the applicable privacy legislation.
The registrar competition model organized by the registry can be regarded as a service to the community at large.
The registry manages the mechanisms for transfers of domains betweenregistrars at the request of the domain holder. This procedure is different from the one known as "change of sponsoring registrar" in the current ..com/.net/.org registry in as much as the registry holds all the domain holder, contact and maintenance information. This provides additional security against accidentally or maliciously initiated transfers affecting data protection.
Outside Sponsoring Organization
The underlying registry-level revenue model is separate from the MDMA revenue model.
The registry-level revenue model is based on cost recovery whereas the MDMA will define its own model based on its own role and process.
MDMA pre-finances the adjustments needed to the CORE SRS to accommodate the specific processes required. Once the registration phase begins, the financial flows are based on the pre-payment principle as follows:
customer -> registrar -> registry operator -> sponsoring organization
MDMA-based pre-screening model
The CORE Registry SRS is being designed to accommodate pre-screening functions performed by outside organizations or individuals appointed and funded by the MDMA. The cost of effective formal pre-screening is normally a multiple of cost of the registry operations.
As soon as a registration is performed, the member registrar's prepayment account is debited. Unless otherwise mandated by the registration policy, no refund takes place if the MDMA’s screening framework rejects the registration. (This principle encourages the submission of well-formed and carefully prepared applications). At regular intervals, the MDMA's portion of registration fees is wired to the MDMA.
MDMA-based post-screening model
The model used in this case is identical to the pre-screening model at the moment of registration, but may involve adjustments when records, deleted, put on hold, cross verified etc.
The charge to the registrar would include the cost-recovery for the Registry operator and the MDMA, including verification costs for acceptance of the application. The renewal process will further be linked to the re-verification of registration data.
Disincentive and special cost recovery charges
Disincentive charges are not designed to have a significant influence on the revenue stream. These charges may be used to manage resource bottlenecks or unexpected high demand for services that would usually be provided free of charge. This business plan does not take into account these charges. Examples of disincentive charges are fees charged to registrars for avoidable repetitive queries in excess of a set limit or ratio. Special cases are fines for accidental registrar transfers and similar problems.
Special cost recovery charges allow the registry to cover the expenses needed for special verifications and actions. They are not expected to have a significant impact on the Registry's financial results because their purpose is precisely to compensate possible perturbations. The idea behind special cost recovery charges is to be able to keep the price low and ensure that considerate customers to not have to pay for those who cause unreasonable costs. Examples of a special cost recovery charge are those applying forre-authentication, for complaint registration or for trademark protection requests (exclusion mechanism).
The CORE registry operator will gradually increase the number of languages in which central information is provided. The current CORE secretariat can currently support members in 5 languages, which in turn facilitates members' outreach in their respective environments. Members will be able to contribute the creation of central multilingual information resources.
Given the fact that CORE has an existing shared registry system and an ongoing registration operations through members, the additional requirements for financial resources can be met through existing funds and equal contributions from new members. The financial requirements for a restricted TLD such as .museum are expected to be relatively low compared to high-volume TLDs.
CORE principal technical resource is its shared registration system (SRS) and the TLD servers. CORE will obtain housing and connectivity from members at market prices based on flexible contracts reflecting actual usage.
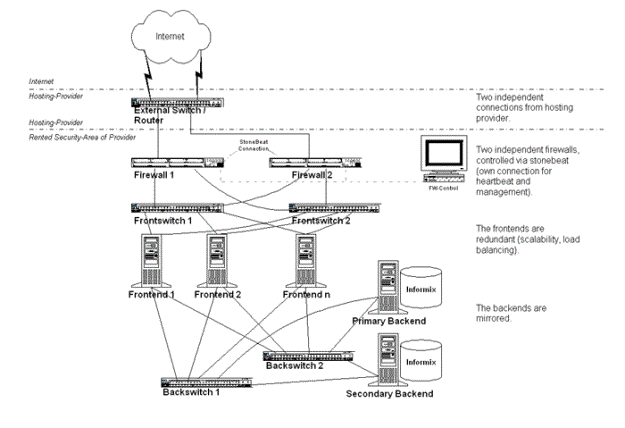
The projected physical plant is composed of a main SRS installation located at a protected co-location site with high-end hardware and network installations. A back-up site is to be hosted by a CORE member as is currently the case. The connectivity available through CORE members is virtually unlimited.
The TLD servers will be distributed and based on a staggered implementation plan. Initially, bandwidth and capacity requirements are modest as long as volume is low.
CORE expects to have 10 staff working for registry activities (including .museum) in various managerial, technical and clerical capacities. This seems credible based on CORE's current operations (800,000 registrations) and the staffing levels of some ccTLD registries in CORE's membership. By way of comparison, DENIC employs 38 staff for over 3,000,000 domains and provides many services centrally that are member-based in CORE's model. Customer service is limited to member support and the provision of neutral information to the public.
An identical configuration though possibly with lesser performance features is used as a test system.
TLD Name servers are based on leased or purchased type hosted at the main SRS site and initially on two, later 5 different locations world-wide. CORE will have full remote access to all TLD servers, housing is to be obtained from members or third parties at market prices.
Whois servers are based on lighter machines easy to duplicate. There will be several Whois servers so at the SRS location, later additional machines will be installed at remote locations. The concept of multiple Whois servers with incremental updating is key for the protection of SRS backend performance. Check queries from members and are directed to specialised Whois servers.
The operational concept of CORE is based on automated tasks on registry level and delegation of value-added tasks to member. This automatically limits the degree to which the registry requires clerical staff and support.
CORE has a tradition of working with members for development work. One-time tasks such as specific software developments and documentation projects can be entrusted to experts from within the compensated at market rates. Many CORE members are specialized application developers who make available their systems to third parties.
While the initial costs are not expected to be a function of volume, running costs allow for adjustments based on the volume experienced.
In case of insufficient funding, the members can assess themselves monthly membership dues.
The members of CORE have used this mechanism since 1998. The mechanism has worked well despite the difficulties and uncertainties to which the association was subject during almost three years. It is reasonable to assume that once the launch of a new TLD is placed under the responsibilityof the association, the peer funding mechanism will work even more smoothly.
The member contributions are credited for future registrations when the financial situation of the registry allows it. As soon as registry funding levels are adequate, members are allowed to run down their contribution level within the limits decided by the membership (see D13.2.12).
Once the required level of cumulated contributions per member has been reduced, the association can reduce the price per registration. All members will always pay the same price irrespective of volumes. The pricing is set in a fashion to ensure sufficient coverage of risks and future costs based on the contractual duration of registrations.
As a not-for-profit membership association, the CORE registry has no special use for business opportunities in its own right. Its purpose is to discharge its duties in an orderly fashion on a cost-recovery basis. However, the current and members of the association, their customers and the public at large have everything to gain from a TLD managed in the public trust and lower registration prices as volumes grow. It is important to point out in this context that CORE is an open association based on non-discriminatory membership criteria.
An additional opportunity for members lies in their ability to co-operate in technical standards while competing in other areas. The shared registry facilitates this productive form of co-competition.
(a) Contractual stipulations at all levels allow for the replacement of the registry in case of failure, but place the same obligations towards domain holders and third parties on the successor organization.
(b) Contracts with infrastructure operators (housing, connectivity providers) contain the obligation to maintain service in case of registry failure for at least 6 months or until a replacing organization can be found. This applies in particular to the TLD server housing providers.
(c) The registry data is backed up and stored at an independent escrow services provider on a daily basis. ICANN or an independent auditor of its choice is enabled to verify the data escrow at any time.
(d) A back-up system is run at a neutral CORE member's site and maintained up-to-date using data synchronization tools.
(e) The regulations of the association allow members to assess themselves contributions to be available for contingencies. Coming from members, they can be made available directly to interim service providers if need be. The amount provided per member can be computed on a "per domain maintained" basis.
(f) The registry operator keeps adequate reserves per domain. CORE is ready to work with ICANN on the concept of a financial escrow arrangement whereby a reserve covering at least 6 months of operation in an emergency is put in escrow with and independent financial institution.
CORE Articles of Association
CORE Rules
Copy of Geneva Company Register certificate
Baloise insurance confirmation
Audit report from KPGM of CORE's 1998 Financial statements based on Internationally Accepted Accounting Principles (IAS)
Audit report from KPGM of CORE's 1999 Financial statements based on Internationally Accepted Accounting Principles (IAS)
Audit report from KPGM of CORE's June 2000 Interim Financial statements based on Internationally Accepted Accounting Principles (IAS)
(CORE is customer of UBS since 1997 and holds funds in excess of USD 3,000,000)
Baloise Assurances Confirmation.
CORE has track record of successful developments in collaborative mode, personnel from various members working together. CORE Registrar SRS operation and maintenance and secretariat have been outsourced to two separate member companies.
It is important to point out that participating members also have extensive experience in shared systems from their own developments. Many member operate shared registration system concepts on their own facilities in order to collaborate with channel partners.
While distributed organizational concept will be maintained to the extent of which projects are posted for member participation, the CORE Registry is directly responsible for the operation of the main SRS site and the Secretariat. The CEO, the CTO and key technical experts are registry staff. Other technical staff members are expected to be seconded part-time or full-time from members. Some experts and consultants employed part-time will be able to work from remote locations.
The existing system demonstrates the ability of CORE’s members to work together (working groups, task forces) despite geographical distances and across diverse types of members companies.
All key systems have fully redundant disk and power supply properties. A backup system can replace the production system withy are located.
Thanks to the use of incremental Whois server updates, the load on the main system is limited to actual domain update transactions. Check queries typically account for over 95 percent of transaction load; this load can thus spread over a range of machine and locations.
It is important to point out that the key requirement for TLD servers is access to expert knowledge in managing them. The multiple TLD servers CORE has access in this context to the experience of CORE member with large zone files such as DENIC with over 3,000,000 domain in the .de zone. The members of the DENIC team participate in the Shared Secondary System project led by CENTR.
Current ICANN Root servers operate with a sustained throughput of about 2 Mega Bits per Second (Mb/sec.) of DNS traffic. CORE TLD servers will be deployed with at least a 2 Mb/sec sustained bandwidth available with a burstable bandwidth initially up to 10 Mb/sec. Understand that the largest Burst sustained for over one minute on a ICANN Root server to date is 12 Mb/sec.
CORE TLD Servers will follow specifications outlined in RFC2010.
CORE will make statistics on availability and performance available to ICANN for periodic review.
The CORE SRS protocol is based on PGP-signed messages exchanged between the SRS and the member registrar. The member registrar can use a stateless interaction client kit (SRSIO), which CORE provides in source code for Unix. SRSIO transparently handles a socket connection to the SRS and as well as the signing and the signature verification on the member registrar side. An API into the CORE Messaging system is under development.
An alternative transport method is email, the use of which must be specifically authorized for a given PGP signature. Email-based submissions are practical for occasional participants such as approval officers in charge of a given area.
The current version of RRP protocol has not been retained because it requires higher transaction capacity of the central system only and works with a registry that does not manage contact and domain registrant information. Although RRP now available as an RFC, it is felt that it was developed without consensus building in a secretive environment.
CORE is ready to participate in constructive standards work, which can involve concepts developed by other existing registries, in particular ccTLD registries. Core supports calls for convergence of shared registry protocols but feels that this deserves to be a technical process and that the registrar constituency is a political, not a technical forum. CORE looks forward to participating in developing IETF standards for the robust Registry Registrar Protocols that can cover all types of TLD management systems.
The SRS design process has always been multilateral and was formalised within CORE’s membership in the SRS working group. The SRS protocol has been the focus of extensive consensus-building process involving dozens of competitors who were able to agree on a common approach.
The first implementation of the CORE SRS was developed based on a call for proposals and contract assigned to Emergent Corporation in November 1997. The system was tested extensively by many CORE registrars during 1998. Members' feedback regarding the first implementation was the basis for the second implementation initiated in January 1999.
CORE is currently using the second implementation of the protocol, developed for CORE by CSL GmbH of Duesseldorf, Germany. The code was rewritten from the start and significant platform changes were made. The current systemhas been designed with Linux as target platform but can run on other Unix version as well. This version was adapted to become a registrar system. The current CORE Registrar system has been running for over one year assisting many organizations to participate in the sail and maintenance of nearly one million domains. CORE was a critical participant in the ICANN sponsored Testbed phase. CORE has played a constructive role in the Testbed phase with overcoming technical issues during the initial phase of implementing a Shared Registry in accordance with NSI/DoC and ICANN.
The database concept has been developed with the following requirements in mind:
The database schema described here covers the tables used to store permanent data, i.e. the current domain, name host, holder and contact information, as well as the respective historic information. Additional tables not described here are used for processing and verification purposes and depend on the specific implementation of the SRS protocol.
Domain table
Used to hold information on the domain itself along with pointers to related tables. Key data elements are the domain name, the registrar in charge of administering the domain, the record creation and last modification date, the domain status (active, lock, hold) and the expiration date of the domain, as well as pointers to the associated contact record for admin contact, technical contact, zone contact, agent for contact and maintenance service provider (maintainer). The purpose of the maintainer pointer is to document the assignment of handling responsibility to resellers or registry members.
Holder table (Registrant)
For each domain there is a domain holder record. The holder data is kept on a separate table because the domain may change while the holder data is not modified; as a result, the holder record last modification date is only affected if indeed there were change to the holder record. (For instance, the change of a name host would affect the domain record, but it would not affect the holder record). The holder table has the same structure as the contact table, but contrary to the latter stands in a strict one-to-one relationship with the domain table. The holder of a given domain is the Registrant.
Contacts table
The contact table is separate from domain table because a given contact can be associated with many domains. For instance, a technical contact is often an employee or role of a service provider and therefore presents in a large number of domain registrations. This is also true for personal domains where an "agent for contact" is specified who may be a different from the domain holder. The contacts are linked to the domain records based on the respective role or quality of the contact. A given contact may be liked to many domains in several qualities at the same time.
Name server or hosts table
A given domain name can be linked to several name server host records. The link between a domain and a name host is based on the name host record identifier, so that it is possible to change the name or the IP number of all domains attached to the same name host record.
There will not be any GLUE generated for hosts not under a SLD with in the zone as specified in RFC2181.
Historic data tables
Historic tables for all the above maintain earlier states of the respective records.
The SRS has been tested with the current configuration at sustained rates of one database update transaction per second involving multiple tables. The system has a built-in queuing mechanism in all internal stages where bottlenecks can appear. As a result, the system can take accept burst load of up to 5 transactions per second in its input queue and process them as capacity becomes available.
It is important to note in this context that the CORE Registry is a "full" or "thick" registry where the contact and registrant data is maintained with the domain and name server data. This feature eliminates the problems associated with Registrar to maintaining a separate Whois data in fracture under widely diverging standards. The advantage to the Registrar, ICANN and the public is that there will not separate Whois Escrow implications for registrars participating with the CORE Registry. Should a CORE Registrar become insolvent, there is no need to reconstitute the registrant´s data as all the data elements are contained in a single registry.
Protocol specificities and the concept of a "thick" registry skew comparative transactional capacity statistics. Transactions in the sense of the CORE SRS and the NSI RRP 1.1.0 are not comparable. The CORE system is designed to handle all data whereas the RRP currently only handles domain name strings and name servers. Current RRP volume statistics are inflated by orders of magnitude through the inclusion of check transactions, which go directly on the RRP interface. (A check transaction a request to verify if a domain is available.) CORE's uses Whois servers (which can easily be multiplied) for these verifications. Even if the Whois server is 30 or 60 seconds behind the back end database, this does not materially increase the likelihood of collisions. Experience shows that the number or requests on the CORE SRS is rather in the same order of magnitude as the number of domains and contacts registered. By contrast, current RRP statistics show for a single day a number of transactions higher than the total number of domain s registered since inception.
The current database concept is expected scale as for tens of million domain records. Additional tuning may be required as the database moves into new orders of magnitude. Since the CORE SRS is based on queuing and distributed computing based on inexpensive Intel hardware, additional equipment can be added to create clustered highly robust path to additional system resources should the need arise. As the TLDs grow in size, additional equipment can be installed to manage the load and availability requirements of increased TLD growth or additional Sponsoring Organizations.
Procedures for object creation, modification and deletion
All database records are created, modified and deleted through request issued and signed by members. Each request contains a template. Usually a given request us used to create, modify or delete a single record.
The details are described in the SRS protocol Specification 1.1 (attached)
See Registration Policy Description and SRS Protocol Specification 1.1.
Where applicable, similar grace period concepts are used as currently in the case of the .com, .net and org, except that, within the constraints of ICANN policies and prescriptions the MDMA, members can decide how they want them implemented and can obtain a change in policy. In particular, the issue of large-scale credit card fraud has been raised. In these cases, the registry will define a policy for investigation and refund if a certain amount is involved in a single case.
Change notification mechanisms are based on the principle that key contact data is in the registry and that in some cases the registry can enhance security and confidence by sending automatic messages in case of changes or other sensitive transactions. This process does not relieve the members of their obligations to manage the interactions with customers.
Statistical and data dump processes run automatically at regular intervals (daily, weekly, and monthly). The reporting times are based on UTC and do not change with daylight savings time.
Given their backgrounds, member registrars are in a good position to analyse their own data. To facilitate checking, the registry makes data dump files available to the members can ensure that their systems are in synchrony.
The registry provides statistical data on an equal treatment basis. The members decide jointly what data they wish to be made available to all members and to the public.
MDMA has access to detailed statistical data.
The registry can generate the following reports.
Name Servers will run the BIND name server as it is widely available in source and runs on many platforms. This is the most actively developed name server software.
Name Servers will have UDP checksums when generating and sending UDP datagrams.
All Name Servers will be dedicated hosts, not having any other dedicated function such as SMTP, NNTP, etc. All logins other than the console will be over encrypted channel such as SSH.
System clocks will be synchronized via the current version of NTP with authentication. At least 2 NTP peers will be used.
Zone transfer access control will be configured so that outbound zone transfers are only permitted to destinations on the servers´ local network and to networks defined by the operators for debugging purposes.
The AXFR protocol will be used to in preference to FTP for zone file distribution. The NOTIFY and IXFR capabilities will be enabled on all Name Servers.
Recursion will be disabled for queries. Interface, User authentication
Each Registrar must maintain an account in good standing. Each Account within the back end system is debited once for each domain/year registered. A delete within the specified grace period will credit the registrars account for the number of domain years related to the registration.
The Registry Operator provides a management interface to MDMA for managing accounts within the backend registry database. This interface is implemented over a secure interface and is implement using the CORE SRS protocol.
All Registrars may inspect their account in real time by issuing protocol level requests or via a Secure Web interface provided by the Registry Operator.
For reliability purposes and to ease members’ cash management, CORE work with financial institutions to either offer the ability to use accounts at several locations with various financial institutions. Members are encouraged to used unique amounts to facilitate tracking of the payments (currently most CORE members wire amounts where the rightmost digits indicate the member number and serial digit used to make sure each amount is different).
The registry secretariat verifies the amounts received over its electronic banking link and credits the amount actually received on the SRS account(referred to as Registrar Credit Units account or RCU account). RCUs are currently equated to one dollar.
As and when credits are used for registrations or other charged-for transactions, the SRS automatically calculates the remaining balance of the RCU account. Conversely, deletions within grace period or the refunds cause the member RCU account to be credited. All transactions are logged.
The RCU balance and the balance of the Registry accounting system are cross-verified per month end. To increase transparency, all figures are based on UTC (GMT) time.
The standard backup data is stored on an Rsync server where it can be accessed a encrypted SSH link. This can be used by the secretariat to crate additional backup copies.
The load on the whois servers is distributed across several systems by the use of a NAT and Firewall and Load Balancing system. The servers are located in a secure facility and adhere to operating system requirements much like those for Name Servers.
The whois service has a limiting device so that denial of service attacks and data mining operations can be defeated.
The whois database can be extended for Sponsoring Organizations, which could allow searching on additional fields such as VAT/EIN or registration number. The Whois system will be compliant with current ICANN policies and procedures.
Remote login into the back-end is limited to times when this feature has been activated temporarily by physical on-site intervention. It is achieved through proxies secure sessions via the front-end machine. The cryptographic keys used for such access are specific to the expert enabled to access the system.
All server hosts will be located in a secure space such as a locked computer room or a data canter with restricted access. The power supplies are redundant, using batteries, generators or other means to protect againstutility power failures. Network connectivity is redundant, so that a single wide area line failure cannot completely isolate the equipment from the rest of the network.
The system and network administrators will educate themselves about potential threats, and stay current on CERT bulletins regarding network break-ins. The system staff will periodically audit the server host's activity logs and be able to detect attempted break-ins during and after the fact.
Moreover, CORE’s organizational model allows it to use incentive-disincentive based load management to ensure considerate and economical use of central resources by members.
To maintain high performance of Whois servers, CORE plans to use restrictions affecting repetitive queries from the same source. Volume users of the CORE whois (e.g. whois portals) need to be identified and specifically authorised. Portals exceeding a certain volume will have to indicate their requestor IP number for each query.
The target availability parameters are set in consideration of relative cost and volume and nature of service provided. Whenever possible, multiple redundant resources are used.
The SRS itself is not for direct use by the public. Member registrars need to be able to determine the amount of money they are willing to spend for the level of availability in time (95%, 99% or 99.9%). Members’ own systems should be designed to accommodate minor outages or slow response times.
The CORE registry will operate with multiple whois servers updated within seconds. While in isolated cases a given domain may be affected by synchronization problems and not show in the whois, the overall whois service can achieve almost uninterrupted availability (barring concerted, large-scale denial-of-service attacks and unexpected surges in demand). If a given whois server is down, users can normally go on another machine. Whois gateway machines run by members can perform the switch automatically if need be. See D15.2.8.
As there will be at least five TLD servers, zero downtime can be achieved as far as the TLD name service is concerned. While high-availability machines are used, the prime quality effort made for an individual server is data integrity and consistency. The measures to protect the integrity are discussed under D15.2.4. and D15.2.5.
In case of failure of a non-redundant components (e.g. a RAID controller), the recovery from backup systems and continuous logs may take up to 8 hours. The main SRS team runs regular fire drills in recovering data from the backup systems to a test system.
While the technical switch over to the backup site can be performed within hours, the decision to switch will only be taken with at least a day advance notice.
The agreements signed by registrars define their minimum support responsibilities towards customers.
The SRS team and the Secretariat support members via email, telephone and via SRS transactions. The Secretariat can interact with members in English, French, German and Spanish; other languages may be added in the future.
If you intend to subcontract any the following:
please (a) identify the subcontractor; (b) state the scope and terms of the subcontract; and (c) attach a comprehensive technical proposal from the subcontractor that describes its technical plans and capabilities in a manner similar to that of the Technical Capabilities and Plan section of the Registry Operator's Proposal. In addition, subcontractor proposals should include full information on the subcontractor's technical, financial, and management capabilities and resources.
It is not expected that any function accounting to more than 10% would be outsourced to a single operator.
The allocation of outsourced is based on due process within the membership. While a series of members have indicated readiness to handle functions and have provided offers therefore, no definitive assignments have been made.
_______________________________
Signature
Werner Staub___________________
Name (please print)
Head of CORE Secretariat_________
Title
CORE Internet Council of Registrars_
Name of Registry Operator
September 30, 2000________________
Date